KNX (standard) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 KNX is an
KNX is an
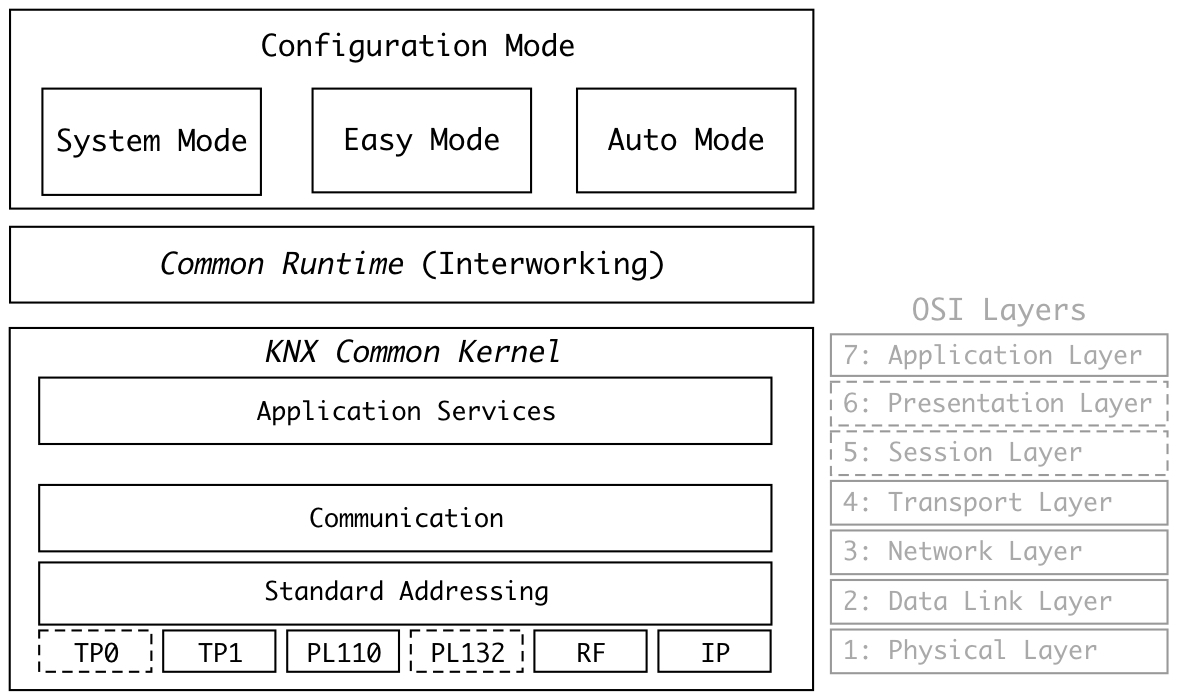 The key features of the KNX architecture are:
* Interworking and distributed application models for the building automation various tasks;
* Schemes for configuration and management of resources on the network, and to permit the binding of parts of a distributed application in different nodes;
* A communication system with a message protocol and models for the communication stack in each node (capable of hosting distributed applications (KNX Common Kernel); and
*Models for the realization of these elements when developing actual devices to be mounted and linked in an installation.
The key features of the KNX architecture are:
* Interworking and distributed application models for the building automation various tasks;
* Schemes for configuration and management of resources on the network, and to permit the binding of parts of a distributed application in different nodes;
* A communication system with a message protocol and models for the communication stack in each node (capable of hosting distributed applications (KNX Common Kernel); and
*Models for the realization of these elements when developing actual devices to be mounted and linked in an installation.
The KNX Association
The KNX (UK) Association
The KNX (Australia) Association
KNX Interface Solutions
{{Authority control Computer buses Building automation Home automation cs:EIBA sq:EIB sistemet
 KNX is an
KNX is an open standard
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a prerequisite to use open license, non-discrimination and extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in the development. There is no single definition ...
(see EN 50090, ISO/IEC
ISO/IEC JTC 1, entitled "Information technology", is a joint technical committee (JTC) of the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC). Its purpose is to develop, maintain and pr ...
14543) for commercial and domestic building automation
Building automation (BAS), also known as building management system (BMS) or building energy management system (BEMS), is the automatic centralized control of a building's HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning), electrical, lighting, ...
. KNX devices can manage lighting, blinds and shutters, HVAC
Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) is the use of various technologies to control the temperature, humidity, and purity of the air in an enclosed space. Its goal is to provide thermal comfort and acceptable indoor air quality. HV ...
, security systems, energy management, audio video, white goods, displays, remote control, etc. KNX evolved from three earlier standards; the European Home Systems Protocol (EHS), BatiBUS, and the European Installation Bus (EIB or Instabus). It can use twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring used for communications in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted ba ...
(in a tree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
, line or star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
topology
In mathematics, topology (from the Greek language, Greek words , and ) is concerned with the properties of a mathematical object, geometric object that are preserved under Continuous function, continuous Deformation theory, deformations, such ...
), powerline, RF, or IP links . On this network, the devices form distributed applications and tight interaction is possible. This is implemented via interworking models with standardised datapoint types and objects
Object may refer to:
General meanings
* Object (philosophy), a thing, being, or concept
** Object (abstract), an object which does not exist at any particular time or place
** Physical object, an identifiable collection of matter
* Goal, an ...
, modelling logical
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises ...
device channels.
KNX standard
The KNX standard has been built on theOSI
OSI may refer to:
Places
* Osijek Airport (IATA code: OSI), an airport in Croatia
* Ősi, a village in Veszprém county, Hungary
* Oši, an archaeological site in Semigallia, Latvia
* Osi, a village in Ido-Osi, Ekiti State, Nigeria
* Osi, Ekiti ...
-based EIB communication stack extended with the physical layer
In the seven-layer OSI model of computer networking, the physical layer or layer 1 is the first and lowest layer; The layer most closely associated with the physical connection between devices. This layer may be implemented by a PHY chip.
The ...
s, configuration modes and application experience of BatiBUS and EHS.
KNX installations can use several physical communication media:
* Twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring used for communications in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted ba ...
wiring (inherited from the EIB standard). (The previously inherited BatiBUS communication medium (TP0) is no longer part of the KNX Specifications.)
* Power-line networking (inherited from EIB standard). (The previously inherited EHS communication medium (PL132) is no longer part of the KNX Specifications.)
* Radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a transmit ...
(KNX-RF)
* IP (also referred to as EIBnet/IP or KNXnet/IP)
KNX is not based on a specific hardware platform and a network can be controlled by anything from an 8-bit microcontroller
A microcontroller (MCU for ''microcontroller unit'', often also MC, UC, or μC) is a small computer on a single VLSI integrated circuit (IC) chip. A microcontroller contains one or more CPUs (processor cores) along with memory and programmable i ...
to a PC, according to the demands of a particular building. The most common form of installation is over twisted pair medium.
KNX is an approved standard by the following organisations, ( inter alia):
* International standard (ISO/IEC 14543-3)
* European standard (CENELEC
CENELEC (french: Comité Européen de Normalisation Électrotechnique; en, European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardization) is responsible for European standardization in the area of electrical engineering. Together with ETSI (telecommun ...
EN 50090 and CEN EN 13321–1)
*US standard (ANSI
The American National Standards Institute (ANSI ) is a private non-profit organization that oversees the development of voluntary consensus standards for products, services, processes, systems, and personnel in the United States. The organi ...
/ASHRAE
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE ) is an American professional association seeking to advance heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration (HVAC&R) systems design and constructio ...
135)
* China Guobiao
The National Standards of the People's Republic of China (), coded as , are the standards issued by the Standardization Administration of China under the authorization of Article 10 of the Standardization Law of the People's Republic of China.
...
(GB/T 20965)
It is administered by the KNX Association cvba, a non-profit organisation governed by Belgian law which was formed in 1999. The KNX Association had 500 registered hardware and software vendor members from 45 nations as at 1 July 2021. It had partnership agreements with 100,000 installer companies in 172 countries and more than 500 registered training centres. This is a royalty-free open standard
An open standard is a standard that is openly accessible and usable by anyone. It is also a prerequisite to use open license, non-discrimination and extensibility. Typically, anybody can participate in the development. There is no single definition ...
and thus access to the KNX specifications is unrestricted.
KNX architectureAll information in this and subsequent sections is summarised from
KNX devices are commonly connected by a twisted pair bus and can be modified from a controller. The bus is routed in parallel to the electrical power supply to all devices and systems on the network linking: *Sensors
A sensor is a device that produces an output signal for the purpose of sensing a physical phenomenon.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a device, module, machine, or subsystem that detects events or changes in its environment and sends ...
(e.g. push buttons, thermostats, anemometers, movement) gather information and send it on the bus as a data telegram;
* Actuators
An actuator is a component of a machine that is responsible for moving and controlling a mechanism or system, for example by opening a valve. In simple terms, it is a "mover".
An actuator requires a control device (controlled by control signal) an ...
(dimming units, heating valves, displays) receive data telegrams which are then converted into actions; and
*Controllers and other logic functions (room temperature controllers, shutter controllers and other)
* System devices and components (e.g. line couplers, backbone couplers).
Classifying devices as either "sensor" or "actuator" is outdated and simplistic. Many actuators include controller functionality, but also sensor functionality (for instance measuring operating hours, number of switch cycles, current, electrical power consumption, and more).
Application software, together with system topology and commissioning software, is loaded onto the devices via a system interface component. Installed systems can be accessed via LAN, point to point links, or phone networks for central or distributed control of the system via computers, tablets and touch screens, and smartphones.
 The key features of the KNX architecture are:
* Interworking and distributed application models for the building automation various tasks;
* Schemes for configuration and management of resources on the network, and to permit the binding of parts of a distributed application in different nodes;
* A communication system with a message protocol and models for the communication stack in each node (capable of hosting distributed applications (KNX Common Kernel); and
*Models for the realization of these elements when developing actual devices to be mounted and linked in an installation.
The key features of the KNX architecture are:
* Interworking and distributed application models for the building automation various tasks;
* Schemes for configuration and management of resources on the network, and to permit the binding of parts of a distributed application in different nodes;
* A communication system with a message protocol and models for the communication stack in each node (capable of hosting distributed applications (KNX Common Kernel); and
*Models for the realization of these elements when developing actual devices to be mounted and linked in an installation.
Applications, interworking and binding
Central to the KNX architecture concepts are datapoints (inputs, outputs, parameters, and diagnostic data) which represent process and control variables in the system. The standardised containers for these datapoints are group objects and interface object properties. The communication system offers a reduced instruction set to read and write datapoint values. Datapoints have to conform to standardised datapoint types, themselves grouped into functional blocks. These functional blocks and datapoint types are related to applications fields, but some of them are of general use (such as date and time). Datapoints may be accessed through unicast or multicast mechanisms. To logically link applications' datapoints across the network, KNX has three underlying binding schemes: one for free, one for structured and one for tagged binding: * In ''free binding,'' links between datapoints are not prescribed - in combination with free addressing, this supports customized multicast grouping at the level of individual datapoints and is central to S-mode configuration (see below); * In ''structured binding,'' the KNX specification stipulates a precise pattern for linking a whole set of datapoints, usually corresponding to a Functional Block or Channel (push-button modes follow this concept); * ''Tagged binding'' is also pre-structured by the application models, but the numerical value of address is part of its value.Common Kernel and Message protocol
The common kernel sits on top of the physical layers and the medium-specific data link layer and is shared by all the devices on the KNX Network. It is OSI 7-layer model compliant: * A general data link layer, which sits above the specific data link layers for each medium, provides access control and the logical link control; * A network layer (for nodes with routing functionality) provides a segment-wise acknowledged telegram (frame
A frame is often a structural system that supports other components of a physical construction and/or steel frame that limits the construction's extent.
Frame and FRAME may also refer to:
Physical objects
In building construction
*Framing (con ...
) and controls the hop count
In wired computer networking, including the Internet, a hop occurs when a packet is passed from one network segment to the next. Data packets pass through Router (computing), routers as they travel between source and destination. The hop count ...
of a frame;
* A transport layer enables four types of communication: one-to-many connectionless (multicast), one-to-all connectionless (broadcast), one-to-one connectionless, one-to-one connection-oriented;
* (OSI session and presentation layers are empty); and
* An application layer offers a toolkit of services to the application process.
Configuration modes
An installation has to be configured at the network topology level and at individual nodes or devices. The first level is a precondition or “bootstrap” phase, prior to the configuration of the distributed applications, i.e. binding and parameter setting. Configuration may be achieved through a combination of local activity on the devices (such pushing a button), and active network management communication over the bus (peer-to-peer, or more centralized master-slave). The KNX configuration mode: * picks out a certain scheme for configuration and binding; * maps it to a particular choice of address scheme; and * completes all this with a choice of management procedures and matching resource realizations. Some modes require more active management over the bus, whereas some others are mainly oriented towards local configuration. There are three categories of KNX devices: *A-mode or "Automatic mode" devices which can configure themselves, and are able to be installed by the end user; *E-mode or "Easy mode" devices that require basic training to install: their behaviour is pre-programmed, but configuration parameters need to be tailored to the user's requirements; or *S-mode or "System mode" devices that can be used to create sophisticatedbuilding automation
Building automation (BAS), also known as building management system (BMS) or building energy management system (BEMS), is the automatic centralized control of a building's HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning), electrical, lighting, ...
systems: they have no default behaviour, and must be programmed and installed by specialists.
KNX encompasses tools for project engineering tasks such as linking a series of individual devices into a functioning installation and integrating different media and configuration modes. This is embodied in an ''Engineering Tool Software'' (ETS) suite.
Devices
A KNX installation always consists of a set of devices connected to the bus or network. Device models vary according to node roles, capabilities, management features and configuration modes, and are all laid down in the profiles. There are also general-purpose device models, such as for bus coupling units (BCUs) or bus interface modules (BIMs). Devices may be identified and subsequently accessed throughout the network either by their individual address, or by their unique serial number, depending on the configuration mode. (Unique serial numbers are allocated by the KNX Association Certification Department.) Devices can also disclose both a manufacturer specific reference and functional (manufacturer independent) information when queried.Logical topology and individual address space
A KNX wired network can be formed withtree
In botany, a tree is a perennial plant with an elongated stem, or trunk, usually supporting branches and leaves. In some usages, the definition of a tree may be narrower, including only woody plants with secondary growth, plants that are ...
, line
Line most often refers to:
* Line (geometry), object with zero thickness and curvature that stretches to infinity
* Telephone line, a single-user circuit on a telephone communication system
Line, lines, The Line, or LINE may also refer to:
Arts ...
and star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
topologies, which can be mixed as needed; ring
Ring may refer to:
* Ring (jewellery), a round band, usually made of metal, worn as ornamental jewelry
* To make a sound with a bell, and the sound made by a bell
:(hence) to initiate a telephone connection
Arts, entertainment and media Film and ...
topologies are ''not'' supported. A tree topology is recommended for a large installation.
KNX can link up to 57,375 devices using 16-bit
16-bit microcomputers are microcomputers that use 16-bit microprocessors.
A 16-bit register can store 216 different values. The range of integer values that can be stored in 16 bits depends on the integer representation used. With the two mos ...
addresses.
* The lowest eight bits provide up to 256 addresses within one line, which can consist of up to four segments, each having a maximum of 64 (TP1-64) devices, or up to 256 (TP1-256) devices. Each segment requires a local power supply and the maximum length of a segment is 1000 m. (The actual number of devices supported is dependent on the power supply and the power load of the individual devices.) Segments connected with line repeater
In telecommunications, a repeater is an electronic device that receives a signal and retransmits it. Repeaters are used to extend transmissions so that the signal can cover longer distances or be received on the other side of an obstruction. Some ...
s can extend to a length of 4000 m and link up to 256 devices.
* Lines may be grouped together into an area, with up to 15 lines connected to a main line via line couplers. The next four bits of the address are used to identify individual lines.
* An entire domain can be formed with 15 areas linked by a backbone line using backbone couplers, and the top four bits of the address space identify an area. (Line repeaters may not be used on a backbone or mainline.)
Coupling units allow address filtering which helps to improve performance given the limited bus signal speed. An installation based on KNXnet/IP allows the integration of KNX sub networks via IP as the KNX address structure is similar to an IP address.
Physical transmission media
TP 1
The TP1twisted pair
Twisted pair cabling is a type of wiring used for communications in which two conductors of a single circuit are twisted together for the purposes of improving electromagnetic compatibility. Compared to a single conductor or an untwisted ba ...
bus (inherited from EIB) provides asynchronous
Asynchrony is the state of not being in synchronization.
Asynchrony or asynchronous may refer to:
Electronics and computing
* Asynchrony (computer programming), the occurrence of events independent of the main program flow, and ways to deal with ...
, character oriented data transfer and half-duplex
A duplex communication system is a point-to-point system composed of two or more connected parties or devices that can communicate with one another in both directions. Duplex systems are employed in many communications networks, either to allow ...
bidirectional differential signaling
Differential signalling is a method for electrically transmitting information using two complementary signals. The technique sends the same electrical signal as a differential pair of signals, each in its own conductor. The pair of conducto ...
with a signaling speed of 9600 bit/s. Media access control
In IEEE 802 LAN/MAN standards, the medium access control (MAC, also called media access control) sublayer is the layer that controls the hardware responsible for interaction with the wired, optical or wireless transmission medium. The MAC sublay ...
is via CSMA/CA
Carrier-sense multiple access with collision avoidance (CSMA/CA) in computer networking, is a network multiple access method in which carrier sensing is used, but nodes attempt to avoid collisions by beginning transmission only after the channel i ...
. Every bus user has equal data transmission rights and data is exchanged directly (peer-to-peer) between bus users. SELV
Extra-low voltage (ELV) is an electricity supply voltage and is a part of the Low voltage bandIEC 61140:2016 Chapter 4.2 in a range which carries a low risk of dangerous electrical shock. There are various standards that define extra-low voltage ...
power is distributed via the same pair for low-power devices. A deprecated specification, TP0, running at a slower signalling speed of , has been retained from the BatiBUS standard but KNX products cannot exchange information with BatiBUS devices.
PL 110
PL 110 power-line transmission is delivered using spread frequency shift keying signalling with asynchronous transmission of data packets and half duplex bi-directional communication. It uses the central frequency 110 kHz (CENELEC B-band) and has a data rate of 1200 bit/s. It also uses CSMA. KNX Powerline is aimed at smartwhite goods
A major appliance, also known as a large domestic appliance or large electric appliance or simply a large appliance, large domestic, or large electric, is a non-portable or semi-portable machine used for routine housekeeping tasks such as cookin ...
, but the take-up has been low. An alternative variant, PL 132, has a carrier frequency centred on 132.5 kHz (CENELEC C-band).
RF
RF enables communication in the 868.3 MHz band for usingfrequency shift keying
Frequency-shift keying (FSK) is a frequency modulation scheme in which digital information is transmitted through discrete frequency changes of a carrier signal. The technology is used for communication systems such as telemetry, weather ball ...
with Manchester data encoding.
IP
KNXnet/IP port 3671 has integration solutions for IP-enabled media likeEthernet
Ethernet () is a family of wired computer networking technologies commonly used in local area networks (LAN), metropolitan area networks (MAN) and wide area networks (WAN). It was commercially introduced in 1980 and first standardized in 198 ...
(IEEE 802.2), Bluetooth
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless technology standard that is used for exchanging data between fixed and mobile devices over short distances and building personal area networks (PANs). In the most widely used mode, transmission power is limi ...
, WiFi/Wireless LAN (IEEE 802.11), FireWire
IEEE 1394 is an interface standard for a serial bus for high-speed communications and isochronous real-time data transfer. It was developed in the late 1980s and early 1990s by Apple in cooperation with a number of companies, primarily Sony an ...
(IEEE 1394) etc.
Frame (telegram) overview
Ignoring any preamble for medium-specific access and collision control, a frame format is generally:Security
KNX Telegrams can be signed or encrypted thanks to the extension of the protocol that was developed starting in 2013, KNX Data Secure for securing telegrams on the traditional KNX media TP and RF and KNX IP Secure for securing KNX telegrams tunnelled via IP. KNX Data Secure became an EN standard (EN 50090-3-4) in 2018, KNX IP Secure an ISO standard (ISO 22510) in 2019.Conformity
Any product labeled with the KNX trademark must be certified to conform with the standards (and thus interoperable with other devices) by accredited third party test labs.See also
*DOLLx8
Digital One Line Link (DOLLx8) is a technology architecture that consists of data communication protocol, synchronous serial data bus and a communication system for embedded systems and electronics. DOLLx8 use ASCII characters in its data prot ...
* EnOcean
The EnOcean technology is an energy harvesting wireless technology used primarily in building automation systems, but also in other application fields such as industry, transportation, logistics or smart homes solutions. The energy harvesting wire ...
* Home automation
Home automation or domotics is building automation for a home, called a smart home or smart house. A home automation system will monitor and/or control home attributes such as lighting, climate, entertainment systems, and appliances. It m ...
* INSTEON
* Z-Wave
Z-Wave is a wireless communications protocol used primarily for residential and commercial building automation. It is a mesh network using low-energy radio waves to communicate from device to device, allowing for wireless control of smart home d ...
* Intelligent building
Building automation (BAS), also known as building management system (BMS) or building energy management system (BEMS), is the automatic centralized control of a building's HVAC (heating, ventilation and air conditioning), electrical, lighting, ...
* Lighting control console
A lighting control console (also called a lightboard, lighting board, or lighting desk) is an electronic device used in theatrical lighting design to control multiple stage lights at once. They are used throughout the entertainment industry and a ...
* Lighting control system
A lighting control system is an intelligent network based lighting control solution that incorporates communication between various system inputs and outputs related to lighting control with the use of one or more central computing devices. Light ...
* OpenTherm
OpenTherm (OT) is a standard communications protocol used in central heating systems for the communication between a central heating boiler and a thermostatic controller. As a standard, OpenTherm is independent of any single manufacturer. A cont ...
* Smart environment Smart environments link computers and other smart devices to everyday settings and tasks. Smart environments include smart homes, smart cities and smart manufacturing.
Introduction
Smart environments are an extension of pervasive computing. Accordi ...
* Touch panel
A touchscreen or touch screen is the assembly of both an input ('touch panel') and output ('display') device. The touch panel is normally layered on the top of an electronic visual display of an information processing system. The display is often ...
* UPB
* Matter (standard)
Matter, formerly Project Connected Home over IP (CHIP), is a proprietary standard for home automation that is royalty-free, with manufacturers only incurring certification costs. Announced on 18 December 2019, Matter aims to reduce fragmentatio ...
, a proprietary, royalty-free standard for integration of home automation equipment
References
External links
The KNX Association
The KNX (UK) Association
The KNX (Australia) Association
KNX Interface Solutions
{{Authority control Computer buses Building automation Home automation cs:EIBA sq:EIB sistemet